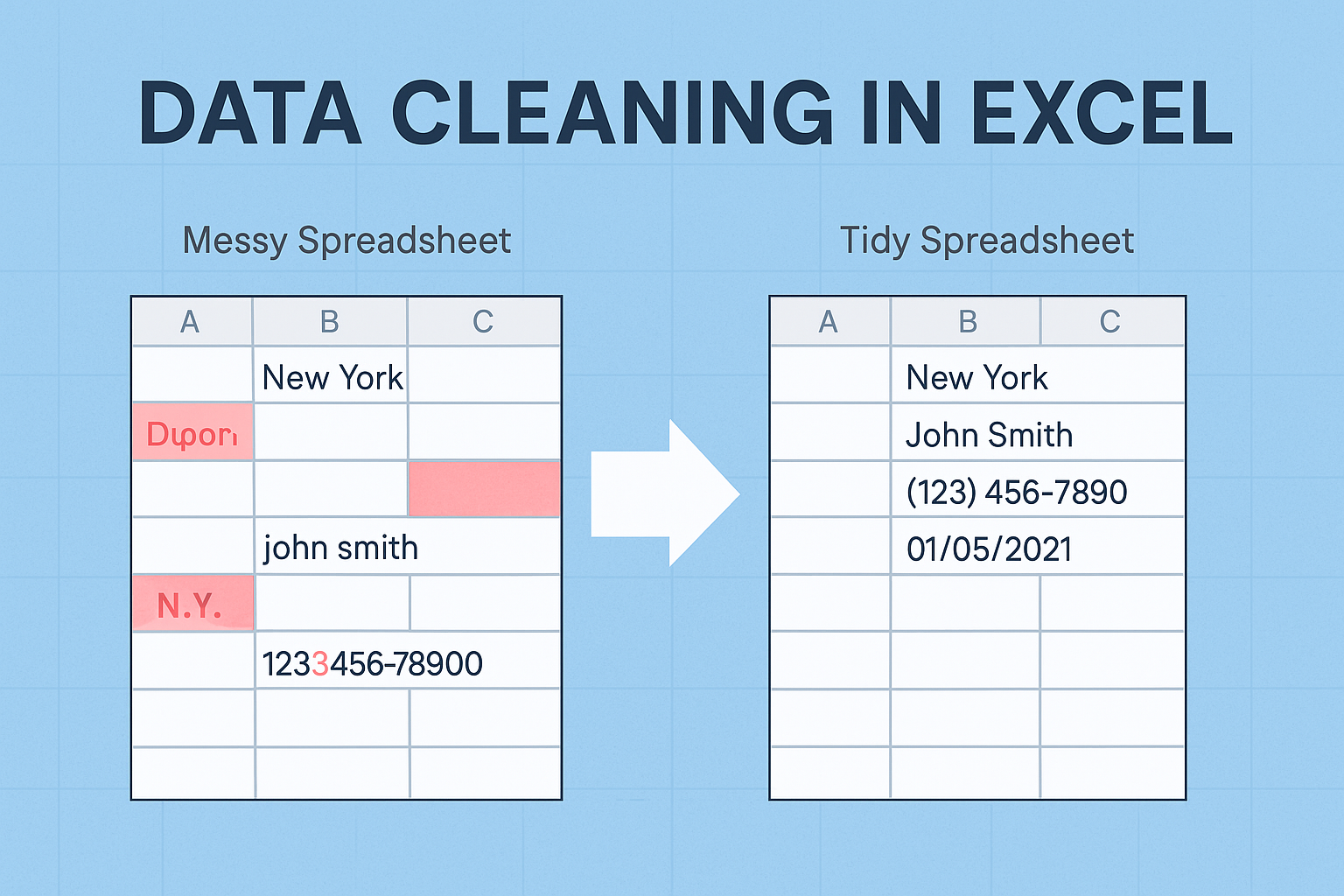
Data Cleaning in Excel is an extremely important topic for beginners. We are aware of how disorganized data can become if we have ever worked with Excel. Messy data is a serious issue, whether it takes the form of missing values, inconsistent names, or random spaces.
Hence, our data must be clean before we can analyze, report, or visualize anything. We’ll go over the best Excel methods for organizing disorganized spreadsheets step-by-step in this approachable tutorial for beginners.
✅ Why Data Cleaning in Excel is Important
Consider the following scenario when examining sales data:
- The spelling of same product names varies, typos basically.
- There are three formats for phone numbers without any need.
- There are some blank rows in between data.
- With minor name changes, the same client shows up five times.
Hence, both our decisions and our conclusions will be incorrect. Cleaning data entails:
- Reporting that is accurate
- Improved understanding
- Reduced mistakes in charts and formulas
Let’s start with data cleaning in Excel –
1. Remove Duplicates
It is common to get some duplicates while we are merging data from multiple sources. But do not worry, Excel does have a built-in function to handle such cases.
🔧 Steps:
-
First select the dataset where we want to remove duplicates
-
Then go to the Data tab
-
After that, just click on Remove Duplicates
-
Then, select the columns to check
-
At last, click OK
💡 Tip: We must always keep a backup copy before we remove duplicates.
2. ✂️ Remove Extra Spaces with TRIM()
Hidden spaces, particularly leading and trailing ones, are frequently present in copy-pasted data. Sorting and filtering are messed up by these. For example – ‘John’ is correct but we also have ‘John___’ and ‘_____John’ in databases. Underscore represents extra spaces.
📌 How to Fix:
-
We should use this formula in a new column against one cell first
-
Then drag it down till entire column we want to trim.
-
Then we can copy and Paste as Values back into the original column
3. ✍️ Standardize Text Format (UPPER, lower, Proper)
It is imperative to avoid inconsistent text formatting as it looks unprofessional and causes duplicate-looking entries in the database.
📘 Use:
-
=UPPER(A1)→ Converts the text in a cell to ALL CAPS -
=LOWER(A1)→ Converts the text in a cell to all lowercase -
=PROPER(A1)→ It capitalizes Each Word (which is fantastic for names)
4. Find & Replace Inconsistencies
We often get inconsistent entries like “NY”, “New York”, and “N.Y.” We can fix these with Find & Replace.
📘 Steps:
-
First Press
Ctrl + H -
Then in “Find what”: we need to type the inconsistent value we are looking to replace
-
Proceed to typing the replacement value in “Replace with”
-
Finish by clicking Replace All
5. 🔢 Convert Text to Numbers
Very often in database, we have numbers stored as text. But these number looking texts will not work in calculations.
👇 We Can:
-
Just click on the warning icon in the cell → Convert to Number
-
Or use:
=VALUE(A1)
6. ⚡ Use Flash Fill for Quick Patterns
We can leverage Flash Fill which detects patterns and can complete columns for us.
📈 Example:
-
We have in Column A: “John Doe”
-
We can in Column B: type “John”
-
Then, Excel will auto-suggest filling down
-
We can now Hit Enter or go to Data > Flash Fill
This is a perfect use case for first / last names, extracting codes and rearranging formats.
7. 🧹 Delete Blank Rows and Columns
Excel formulas stop running when they come across blank rows and columns and also distort Pivot Tables.
🧽 Clean-Up:
-
First select the sheet
-
Then, press
Ctrl + G→ Special -
Now choose Blanks → OK
-
Complete this by right-clicking a selected row/column → Delete
8. 🕳 Handle Missing Values
We will also come across empty cells while doing data cleaning in Excel. We should not ignore empty cells, rather we should decide if they are intentionally there or by mistake.
🔧 Options:
-
Delete rows if too many cells are missing
-
Fill with “Unknown”:using the IF formula. Learn more on IF formula here – How to use IF formula in Excel
-
We can also fill down previous values for time-based data
9. 🚧 Use Data Validation to Prevent Errors
This is a pro active step which prevents users from entering incorrect values. We are basically stopping bad data from entering the sheet by using Data Validation. For e.g., if we set a rule for any column, that we can enter only one of these 3 values – ‘John’, ‘Mary’ or ‘Phillips’. Now if someone tries to write ‘Johnn’, which seems to be a typo, they will not be able to and they will get an error message.
🎯 To Allow Only Dates:
-
First select cells
-
Then go to Data > Data Validation
-
Now choose Date
-
Complete by setting a date range
Other use cases:
-
We can set the rule to be able to enter numbers only
-
We can provide a list of allowed entries. This list pops us as a drop down and user has to choose from these values only.
-
Max/min text length
10. 🔗 Split Data with Text to Columns
We can use this feature of data cleaning in Excel to separate names, addresses, or codes. For e.g., we can split ‘John Doe’ as ‘John’ in one column and ‘Doe’ in another.
🧾 Steps:
-
First select the column we want to split
-
Then go to Data > Text to Columns
-
Now choose Delimited (e.g., space, comma)
-
Select delimiter → click Finish
11. 🔍 Use Filters to Spot Errors
As the most basic technique of data cleaning in Excel manually, we can use Filters to help us identify blanks, duplicates and unexpected entries.
➕ Use:
-
Start by selecting header row
-
Click on Data > Filter
-
Now we can sort / filter each column for insights
12. 🎨 Highlight Problems with Conditional Formatting
We can see issues instantly with the help of color-coded formatting.
🌈 Try This:
-
First select your data
-
Then go to Home > Conditional Formatting
-
Now we need to choose “Duplicate Values”, “Blanks”, “Greater/Less Than”, “Custom formula rules” and choose the color we want to highlight with.
13. 📝 Run Spell Check on Text Columns
As expected, when multiple people work on a single Excel, Names, cities, and product names can have typos.
🔍 Shortcut:
-
Press
F7or go to Review > Spelling
By doing this, we will not be able to fix all issues, but it’s definitely a helpful step.
14. 🧠 Flag Issues with Simple Formulas
Write simple checks to catch mistakes.
Examples:
-
Flag non-numbers with ISNUMBER and IF. IFNUMBER tells us if we have number in a particular cell. We can combine the result with IF to flag errors.
-
Check ranges by combining IF with AND formula. Learn about AND formula here – How to use AND formula in Excel
15. 🧰 Try Power Query for Advanced Cleaning
Power Query (under Data > Get & Transform Data) is Excel’s powerhouse for:
-
Regularly cleaning and reshaping large datasets
-
Doing automation of cleaning steps
-
Combining multiple sources
It may take some practice to learn, but it’s a game-changer when you’re ready. We can learn more on this here —Power Queries in Excel
16. 🤖 Automate with Macros
Using a Macro will be a great relief if we need to repeat the same data cleaning in Excel steps weekly.
🛠 How to Record:
-
Go to View > Macros > Record Macro
-
Now perform the cleaning steps
-
Stop recording
We can now perform clean up of similar files in seconds. Learn more on this here – Using Macros in Excel for Data Cleaning
17. 📛 Use Named Ranges and Tables for Smarter Formulas
We can make our formulas fun and easier to read and maintain with named ranges:
-
Define names:
Formulas > Define Name→ Use=SalesAmountinstead ofB2:B1000 -
Convert to Table:
Ctrl + T→ Use=Table1[Amount]and formulas stay dynamic
Named ranges can reduce errors and make formulas more self-explanatory.
18. 🧮 Use Dynamic Arrays (Excel 365+)
We can leverage dynamic array functions which let us work smarter rather than work harder.
📌 Examples:
-
We can use below formula to remove blanks:
=FILTER(A2:A100, A2:A100<>"") -
This formula can extract unique values from a row or column:
=UNIQUE(A2:A100) -
We can sort data by:
=SORT(A2:A100)
These formulas can auto-expand and they also auto update as our data changes.
📌 Final Checklist: Your Toolkit on Data cleaning in Excel
| Task | Excel Tool / Function |
|---|---|
| Remove duplicates | Data → Remove Duplicates |
| Extra spaces | =TRIM() |
| Text formatting | =UPPER() =PROPER() etc. |
| Replace values | Ctrl + H |
| Text to numbers | =VALUE() or cell alert |
| Pattern filling | Flash Fill |
| Blank row removal | Go To Special |
| Missing values | =IF() or fill down |
| Error prevention | Data Validation |
| Text splitting | Text to Columns |
| Visual inspection | Filters + Conditional Format |
| Spelling errors | F7 |
| Logic checks | =IF(), =ISNUMBER() |
| Advanced cleanup | Power Query |
🎉 Final Thoughts on Data cleaning in Excel
Data cleaning in Excel is not a very difficult task. We can turn jumbled, unreliable spreadsheets into tidy, analysis-ready datasets using a few simple Excel tricks.
Learn the fundamentals first, practice frequently, and gradually discover new tools like Power Query. Once we learn advance techniques like writing complex formulas, using Macros and VBA code and Power Query, we will be able to clean up much faster. We should also use data validation rules to avoid typos and wrong data from entering the sheet in first place.
Your manager and future self will appreciate it.
Also check out our other articles –
Awesome.
Very good https://is.gd/N1ikS2
Awesome.
Cool.